First, it’s important to understand that there are two types of sitemaps:
- XML sitemaps
- HTML sitemaps
1. XML Sitemap
An XML (Extensible Markup Language)Sitemap is specially written for search engine crawler. A search engine crawler can quickly and easily extract all the important piece of information about your site by looking at the XML file.
In simple terms, an XML sitemap is a list of your website’s URLs.
A Sitemap is an XML file that lists URLs for a site along with additional metadata about each URL, such as, when it was last updated, how often it usually changes, and how important it is? So that search engines can more intelligently crawl the site.
It acts as a roadmap to tell search engines what content is available and how to reach it.
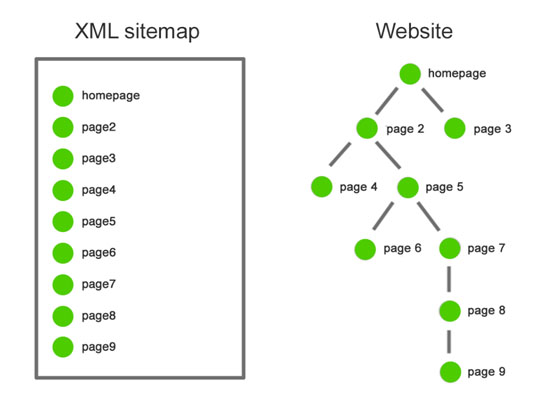
In the example above, a search engine will find all nine pages in a sitemap with one visit to the XML sitemap file.
On the website, it will have to jump through five internal links to find page 9.
XML Sitemap Format
The Sitemap must,
- Begin with an opening <urlset> tag and end with a closing </urlset> tag.
- Specify the namespace (protocol standard) within the <urlset> tag.
- Include a <url> entry for each URL, as a parent XML tag.
- Include a <loc> child entry for each <url> parent tag.
All other tags are optional. Also, all URLs in a Sitemap must be from a single host.
The following example shows a Sitemap that contains just one URL and uses all optional tags.
Code Sample
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”UTF-8″?>
<urlset xmlns=”http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9″>
<url>
<loc> http://www.example.com/ </loc>
<lastmod> 2020-01-01 </lastmod>
<changefreq> monthly </changefreq>
<priority> 0.8 </priority>
</url>
</urlset>
XML Sitemap Generator Tool (Website)
XML Sitemap Tags
1. <urlset>
It references the current protocol standard.
2. <url>
This is a parent tag for each URL entry. The remaining tags are children of this tag.
3. <loc>
It is a URL of the page. This URL must begin with the protocol, such as http or https and end with a trailing slash (/), if your web server requires it.
4. <lastmod>
This is a date of last modification of the file. This date should be in YYYY-MM-DD format.
5. <changefreq>
How frequently the page is likely to change.
Valid values are:
- always
- hourly
- daily
- weekly
- monthly
- yearly
- never
The value “always” should be used to describe documents that change each time they are accessed. The value “never” should be used to describe archived URLs.
6. <priority>
This is the priority of URL, relative to other URLs on your site. Valid values range from 0.0 to 1.0
2. HTML Sitemap
An HTML sitemap is an HTML page on which all subpages of a website are listed. It is usually linked in the footer of a site and is therefore visible to all visitors.
XML sitemaps take care of search engine needs. HTML sitemaps are mainly created for users, as they help them to get an overview of the structure of your site and to navigate through all the subpages.
An example of a clearly arranged sitemap can be found on amazon.com.
https://www.amazon.com/gp/site-directory
This sitemap contains all the main categories as well as the most important subcategories, making it easy for users to navigate through the site.
HTML sitemaps are of great importance for usability of websites, as they enable users to access any subpage quickly. HTML sitemaps can also be useful with regard to search engine optimization (SEO), as they make it easier for Google and other search engine crawlers to find all subpages. Since an HTML sitemap consists of internal links, search engines crawlers like Google Bot follow these links so they can reach all subpages in just a few steps.



























Add comment